
"It makes people a bit more independent from the grid when we tend to see big spikes." And at night, the batteries will serve their houses instead of the grid," Quirk said. "If people have solar as well as a battery, they can use the solar in the day to feed their houses and charge their batteries. While solar batteries are a must for an off-grid solar system, they provide benefits to any solar system. How solar batteries can help you (and the grid)Įnergy storage will make it easier for you to rely on solar energy even when the sun isn't shining. "If everyone goes solar, then the grid has too much electricity in the summer and not enough in the winter." "We have to understand the grid's perspective," Quirk said. The duck curve deepens as more solar panels overgenerate during off-hours but taper off as the sun goes down and demand for electricity spikes. Solar panels operate best in direct sunlight, typically in the middle of the day - which is also when demand for electricity is lowest. Plotted on a graph, it looks like a duck. The duck curve is a measure of solar power generation and energy demand. Particularly during the shorter days of winter when solar power generation becomes less effective, people rely more on the grid during peak hours, steepening what's known as the duck curve. When solar panels aren't able to produce enough energy, homeowners have to draw from the grid - adding to the strain on the grid's system. In the same way solar panels can smooth out peaks in the grid's supply curve, they can also stress it. By adding to the utility's power supply during peak demand, solar panels help to smooth out that spike. When the sun is shining and solar panels produce more energy than a home can use at one time, that excess energy flows back into the market. That's where net metering comes into play.
CONNECTING INDEPENDENT SOLAR GRIDS TO GRID INSTALL
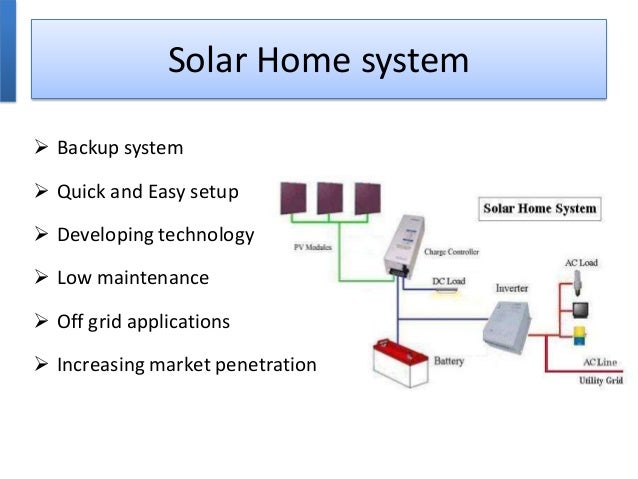
Some homeowners also choose to install back-up generators. Depending on the size of your home and your energy needs, you may need more than one battery. An off-grid solar array requires an extensive energy storage system to ensure you don't experience power failure during periods of low sun exposure. If you opt for an off-grid solar system, you will be responsible for meeting your own energy needs. When your panels are less productive, you'll draw from those stores as you would the grid through net metering. An off-grid solar system runs independently by generating electricity and storing that power in batteries. With an off-grid solar system, you will have no physical power lines or wires leading to your home (except from your own solar panels), nor will you receive any bills from a utility company or retail electric provider. People who live in remote locations or who want to use 100% clean energy may lean toward off-grid systems. However, your utility may charge you connection fees.

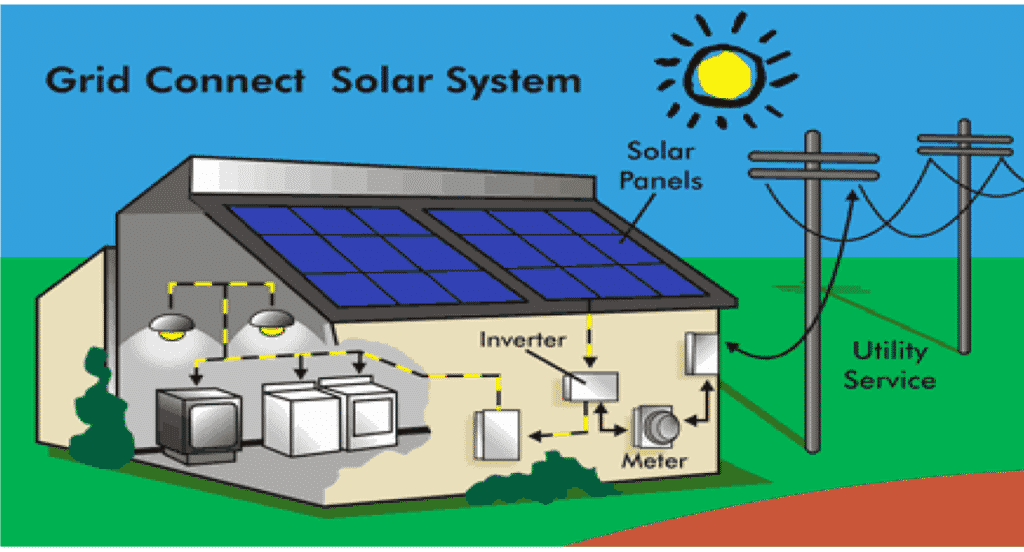
Because you won't rely entirely on your panels for all your energy needs, there are typically fewer upfront costs in the form of energy storage systems. Grid-tied solar systems tend to be the cheapest and most flexible option. Since solar panels rely on sunlight to generate power, this is particularly important if you live in an area that frequently experiences overcast or rainy days. This allows you to draw electricity from your utility company as needed. Grid-tied solar systemĪs the name implies, grid-tied systems are connected to the electrical grid via net metering, which allows for two-way movement between your solar array and the grid, or another method. Read on to learn about their differences. Most solar panels are integrated with the grid, according to a 2015 study from the MIT Energy Initiative. The relationship between your solar system and the electricity grid determines whether you're a self-sustaining energy producer or you rely, at least partially, on public energy. What is the relationship between your solar system and the grid? Programs like net metering, in which your utility pays you for excess power you send to the grid, and the use of batteries allow utility companies to work in tandem with solar panel owners - a move that experts said is mutually beneficial. Understanding how solar panels and the grid work together can help you decide if you want to be energy self-sufficient or grid-dependent.
The US electric grid, a network of power plants, transmission lines and distribution centers, provides power to more than 150 million customers nationwide. Whether you want your solar panels to operate in tandem with the grid or not is something to consider when shopping for solar panels. Off-grid systems place you on your own solar island, which means you'll be responsible for producing all of your own energy. Grid-tied systems have a give-and-take relationship with the wider electrical system, drawing from it when needed and sending excess energy back. Going solar doesn't mean going off the grid - unless you choose to.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
